Have you ever run your tongue over a tooth and felt that tiny rough spot — that little “dip” that makes you wonder if it’s a cavity forming?
It’s that sinking feeling: you know a trip to the dentist is looming, but you secretly hope there’s another way.
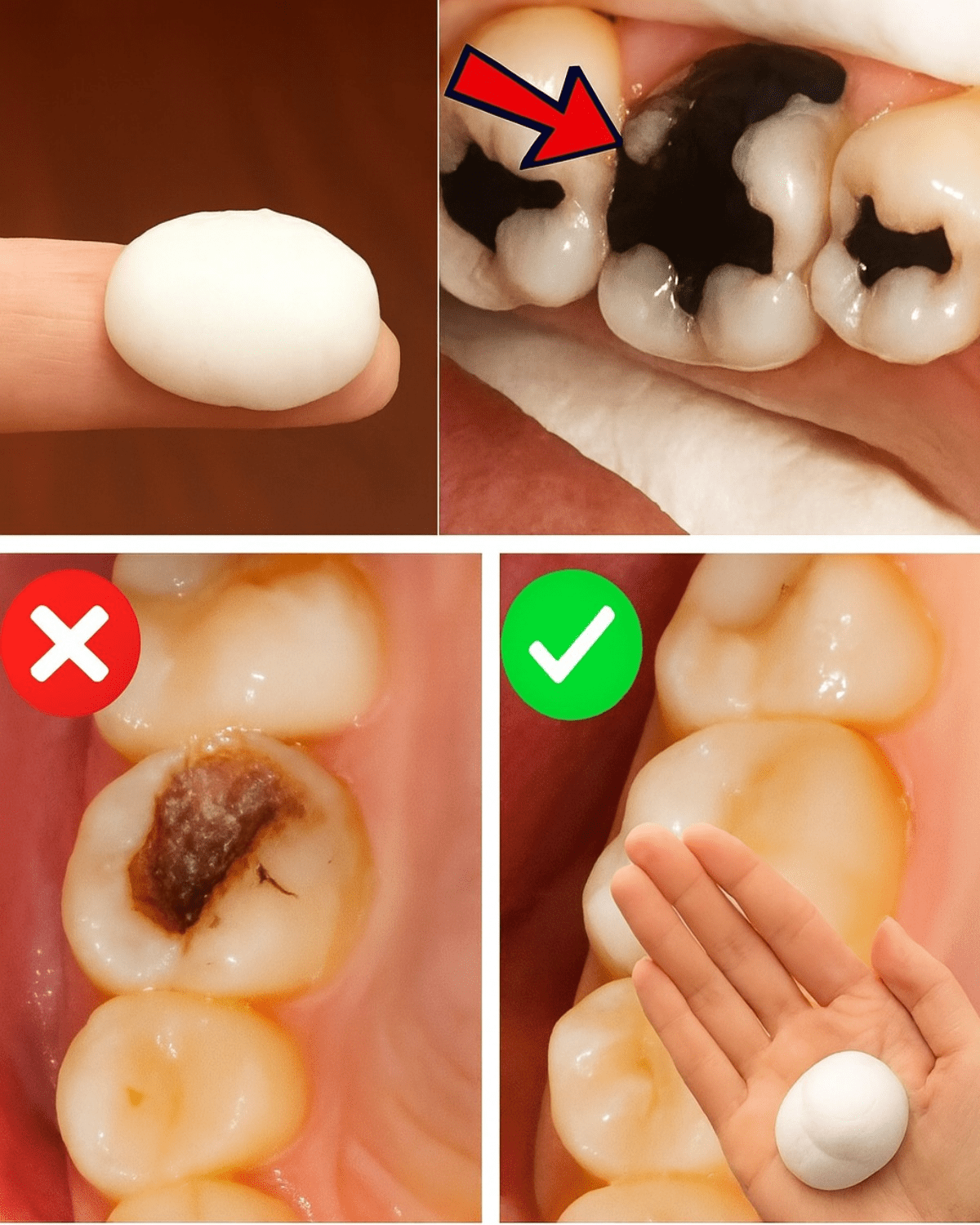
The truth is, while advanced cavities need professional care, your body has a remarkable ability to repair early-stage enamel damage — if you give it the right tools.
Let’s explore how to strengthen your teeth naturally and keep that dentist drill far, far away.
1. Feed Your Enamel the Right Minerals
Your teeth are alive — filled with nerves, blood flow, and living cells. When the enamel weakens, it’s often because minerals like calcium and phosphorus have been stripped away by acids from food or bacteria.
But here’s the good news: remineralization can happen.
By eating foods rich in these minerals, you’re giving your enamel the raw materials it needs to rebuild.
Try adding:
- Cheese and yogurt (natural calcium and casein phosphopeptides that protect enamel)
- Leafy greens like kale and spinach (plant-based calcium and magnesium)
- Bone broth or sardines (phosphorus and collagen for deeper tooth support)
Think of it as feeding your teeth from the inside out.
2. Rinse Away the Acid Attack
Every time you eat, bacteria feed on leftover sugars and produce acids that eat away at your enamel.
The longer those acids sit, the more damage they cause.
A simple trick? Rinse your mouth after meals with water or salt water.
Salt helps balance oral pH and has mild cleansing properties.
And if you love citrus, soda, or coffee — try not to brush right after consuming them.
Wait 20–30 minutes so your enamel can re-harden before brushing.
3. Oil Pulling — The Ancient Detox for Your Mouth
It might sound strange, but swishing a spoonful of coconut oil in your mouth for 10–15 minutes can do wonders.
This ancient Ayurvedic practice helps reduce harmful bacteria and may promote a cleaner, fresher oral environment.
Coconut oil also contains lauric acid, which has natural antimicrobial effects — perfect for reducing plaque and supporting gum health.
Try it once a day in the morning before brushing. You might be surprised by how smooth your teeth feel afterward.
4. Vitamin D: The Missing Link in Tooth Health
Even if you eat calcium-rich foods, your body needs vitamin D to absorb that calcium efficiently.
Without it, the minerals simply pass through your system unused.
Spend 10–15 minutes in sunlight daily or consider vitamin D–rich foods like:
- Salmon, tuna, or sardines
- Egg yolks
- Fortified plant milks
Low vitamin D levels have been linked to weaker enamel and higher cavity risk — so think of sunshine as a natural dental supplement.
5. Balance Oral pH with Natural Helpers
A balanced mouth pH (around 7.0) is your first defense against decay.
When acidity spikes below 5.5, enamel starts dissolving.
Here’s how to keep things balanced:
- Chew sugar-free gum with xylitol — it boosts saliva flow and neutralizes acids.
- Drink green tea — it’s full of catechins that fight oral bacteria.
- Eat crunchy veggies like celery and carrots — they clean teeth and stimulate saliva.
Every small habit adds up to a healthier, more resilient smile.
6. Remineralizing Toothpaste — A Natural Boost
Look for toothpaste with:
- Hydroxyapatite (a natural form of calcium used in enamel)
- Xylitol (helps reduce cavity-causing bacteria)
- Aloe vera or green tea extract (soothing for gums)
These ingredients may gently assist enamel repair while keeping your mouth fresh and balanced.
If you prefer a DIY option, some people use a gentle paste made of baking soda, coconut oil, and a pinch of calcium powder a few times a week — but always check with your dentist first if you have sensitivity.
7. Watch Out for the Silent Enemies: Snacking and Dry Mouth
Constant snacking means constant acid production.
Each time you eat, bacteria feast — and enamel weakens a little more.
Try spacing meals 3–4 hours apart to let your saliva neutralize acids naturally.
If your mouth feels dry often, hydrate well and consider chewing sugar-free gum to trigger saliva flow.
Saliva isn’t just moisture — it’s nature’s protective shield, packed with minerals that rebuild enamel 24/7.
8. Case Study: From Sensitivity to Strength
Mary, 54, had mild sensitivity on her upper molars — that “zing” whenever she drank cold water.
Instead of rushing to the dentist, she made small changes: oil pulling, daily spinach, more cheese, and less soda.
Three months later, her sensitivity was gone.
Her dentist confirmed: no new cavities, enamel hardness improved.
While everyone’s experience is unique, Mary’s story shows what’s possible when you work with your body’s natural repair system.
9. Your Nighttime Routine Matters Most
While you sleep, saliva production slows — leaving your teeth more vulnerable.
That’s why what you do before bed matters.
Try this routine:
- Rinse with salt water.
- Brush with remineralizing toothpaste.
- Oil pull or apply a drop of coconut oil to problem spots.
- Avoid late-night sugary snacks.
Think of it as “night repair mode” for your teeth.
10. When to Seek Help
Natural methods can help strengthen enamel and slow decay, but they can’t reverse deep cavities that reach the dentin or pulp.
If you feel pain, sensitivity, or see dark spots that grow — don’t wait.
Early professional care can save your tooth from extraction or root canal.
But here’s the beautiful part: the earlier you act naturally, the less likely you’ll ever need that drill.
Final Thoughts
You don’t need fancy products or expensive treatments to start improving your oral health — just consistent, mindful habits.
Feed your enamel. Neutralize acids. Support your body’s ability to heal.
Because the real secret to avoiding the dentist isn’t fear — it’s empowerment.
Every choice you make today shapes your smile tomorrow.
So tonight, when you brush your teeth, remember: your mouth isn’t just cleaning — it’s healing.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional dental or medical advice. Always consult a licensed dentist for personalized recommendations.